Feeling hot and bothered? It’s not the humidity, it’s the dew point
19 April 2017
Do you sometimes feel much warmer than the actual observed temperature? ‘It’s not the heat, it’s the humidity’, right? Well not always – at higher temperatures that oppressive, muggy feeling can actually be more about dew point than humidity.

What is dew point?
Dew point is the temperature to which air must be cooled in order to produce condensation (dew). It represents how much moisture is in the air. The higher the dew point temperature, the greater the atmospheric moisture content.
What’s the difference between dew point and humidity?
They both measure moisture in the air, but dew point is related to the quantity of moisture, while relative humidity expresses how close the air is to saturation. Relative humidity is the amount of moisture as a percentage of the amount that air can hold – and warmer air can hold more moisture than cooler air. So, if the amount of moisture in the air stays the same but the temperature rises, the relative humidity falls. Conversely, if temperature falls, relative humidity rises.
Because of its direct relationship to fluctuating temperature, relative humidity doesn’t provide suitable guidance on how much moisture is available at a specific location. Dew point however, is relatively consistent – unless affected by weather systems, such as troughs and fronts. For this reason, meteorologists prefer to use dew point when analysing atmospheric moisture and inferring what the conditions may feel like – represented by the apparent (‘feels like’) temperature.
How does dew point affect the temperature you feel?
In warm, sultry weather, moisture in the air can impede your body’s ability to cool down. One of the ways your body cools itself is by the evaporation of moisture from your skin. When the air is moist, this process slows down and you feel hotter for longer. So the higher the dew point, the longer it takes for your body to cool itself.
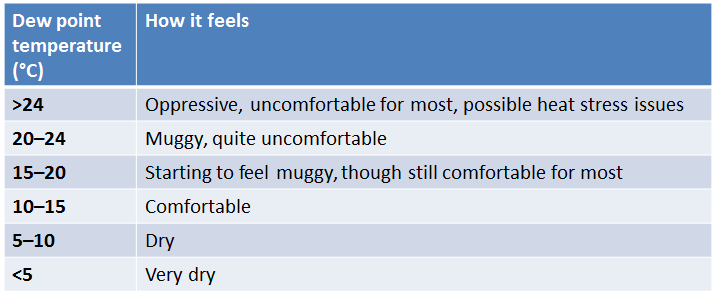
How you experience dew point varies, depending on your metabolism and the conditions you’re accustomed to, but it is possible to create an index of how an average person may feel at a certain dew point. This one uses Brisbane’s climate as an example.
If you’re used to the tropics, you may find the ranges in this scale low, particularly during spring and summer where dew points are commonly above 24 °C. On the other hand, if you’re from southern Australia, you might find these ranges high.
So that old adage might better run, ‘It’s not the heat, it’s the moisture in the air, which at higher temperatures is more reliably indicated by dew point than humidity’. Think it will catch on?
Viewing dew point observations and forecasts
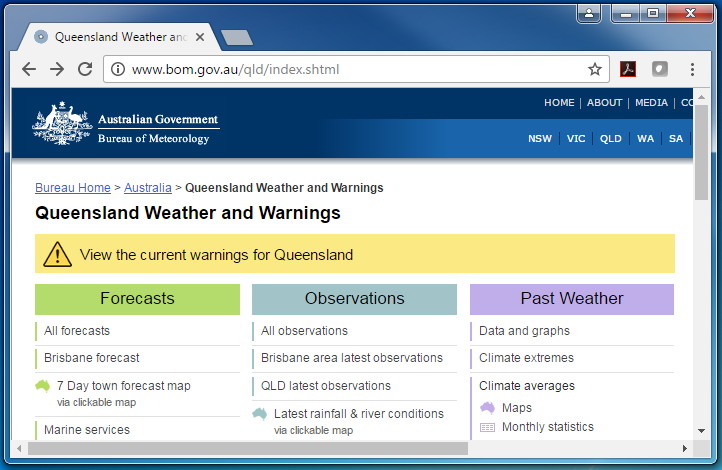
We provide current dew point analysis on our website, on the observations page for each state/territory. To check the latest dew point temperature for a given location, open the page for your state/territory and under ‘Observations’ click ‘latest observations’.
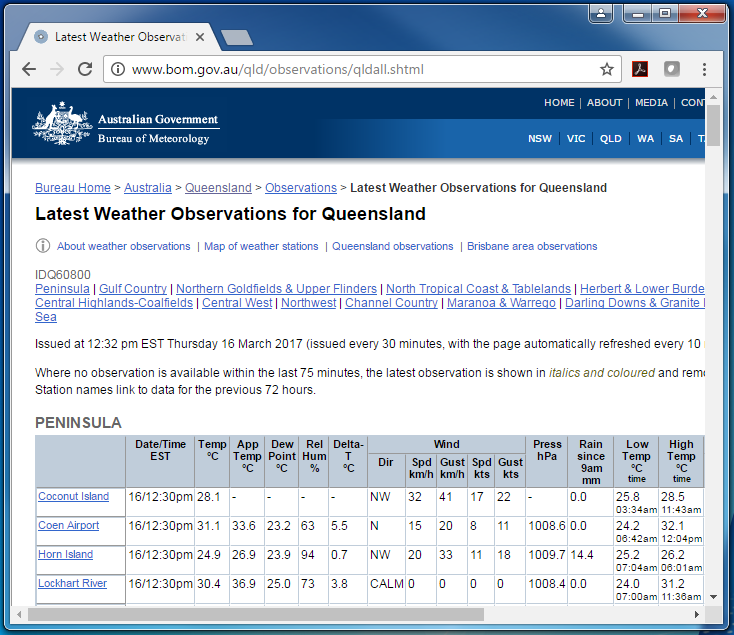
You can see the dew point temperature, along with all the latest observations.
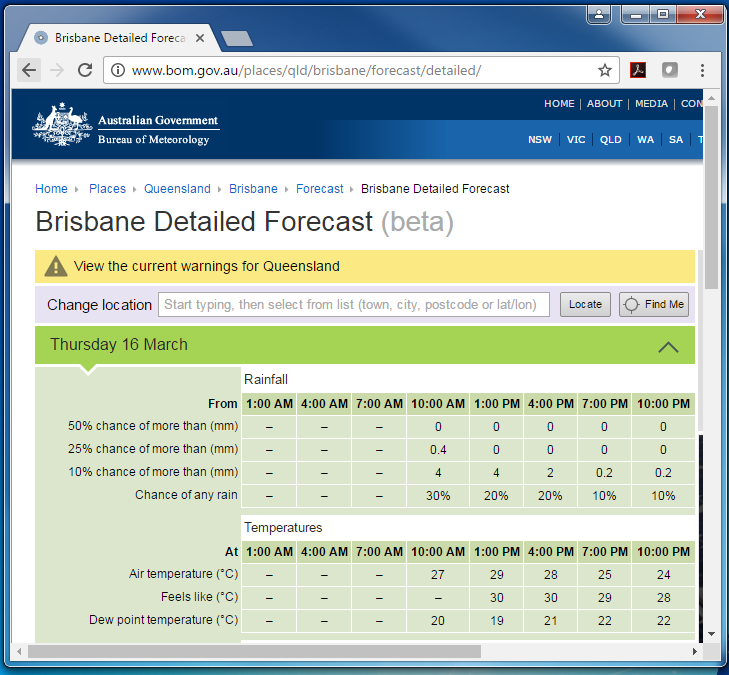
You can also check the dew point forecasts at 3 hourly intervals for the next 7 days. Type the place name into the MetEye search box, click ‘Locate’ and ‘See text views for location’, then click ‘Detailed 3-hourly forecast’.



Comment. Tell us what you think of this article.
Share. Tell others.