2018–19 was Australia's hottest summer on record, with a warm autumn likely too
01 March 2019
Australian summers are getting hotter. Today marks the end of our warmest summer on record, setting new national temperature records. Worsening drought, locally significant flooding, damaging bushfires, and heatwaves capped a summer of extremes. As we look to autumn, warmer temperatures overall and below-average rainfall—especially in eastern parts of the country—are likely.
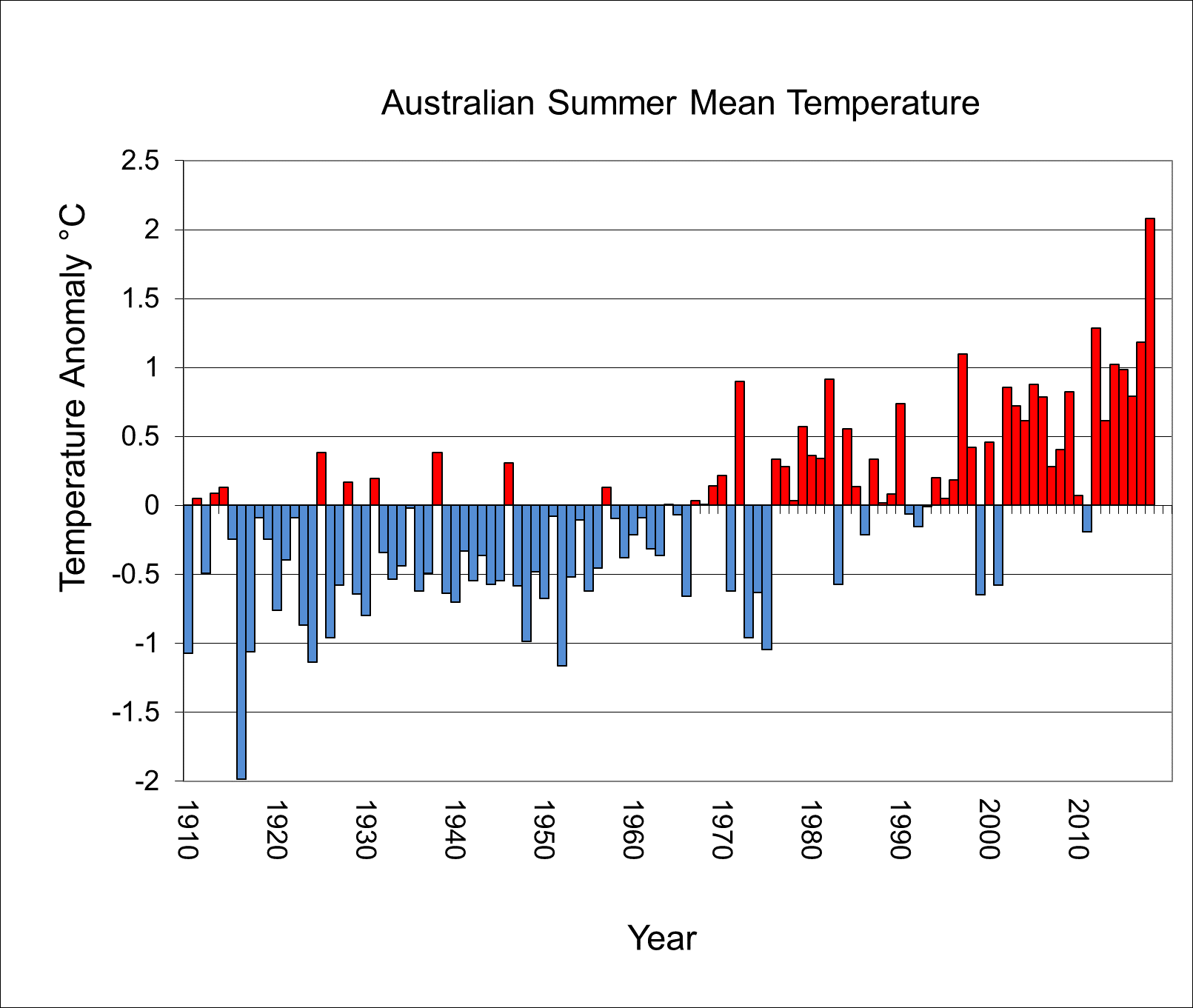
Graph: Australian summer mean temperature anomalies against the 1961–1990 average.
Very hot…
The starkest feature of this summer was the record warmth. The national average temperature was 2.14 °C above average, easily beating the previous record high set in summer 2012-13 (which was 1.28 °C warmer than average).
Very low rainfall accompanied the record heat of summer. At the national scale, each month was notably dry, and total summer rainfall was 32 per cent below average, the lowest for summer since 1982–83. The monsoon onset was delayed in Darwin until 23 January (the latest since 1972–73) and typical monsoonal weather was absent for most of summer.
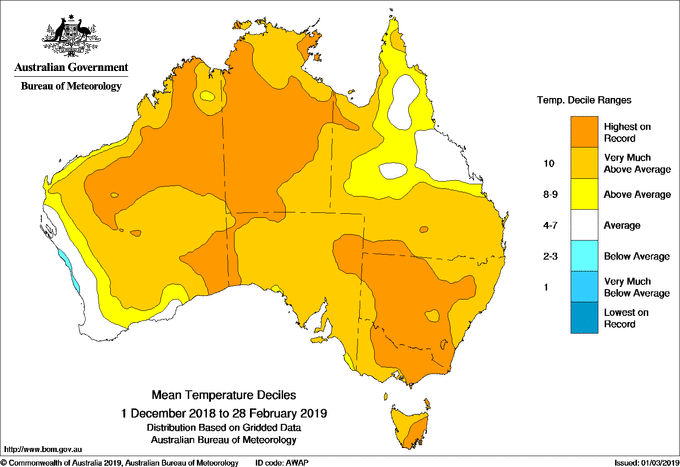
Map: Summer 2018–19 mean temperature deciles.
In December 2018 Australia saw its highest mean, maximum and minimum temperatures on record (monthly averages, compared to all other Decembers). Notable heatwaves affected the north of Australia at the start of the month, spreading to the west and south during the second half of December. Temperatures peaked at 49.3 °C at Marble Bar in Western Australia on the 27th, with mid-to-high 40s extending over larger areas.
The heat continued into January, which set a national monthly mean temperature record at 2.9 °C above the 1961–1990 average. Heatwave conditions which had emerged in December persisted, with a prolonged warm spell and numerous records set. Eight of the ten hottest days for the nation occurred during the month, while a minimum temperature of 36.6 °C at Wanaaring (Borrona Downs) in western New South Wales on the 26th set a new national minimum temperature record.
Temperatures moderated a little in the east of the country for February, partly in response to flooding rainfall in tropical Queensland. Even so, the national mean temperature is 1.38 °C above average, making this February the fourth warmest on record.
…and very dry
Australia has seen dry summers before and many of these have been notably hot. The summers of 1972–73 and 1982–83—which featured mean temperatures 0.90 °C and 0.92 °C above average, respectively—both came during the latter stages of significant droughts, and were both records at the time.
As the State of the Climate 2018 report outlines, Australia has warmed by just over 1 °C since 1910, with most warming occurring since 1950. This warming means global and Australian climate variability sits on top of a higher average temperature, which explains why 2018-19 was warmer again.
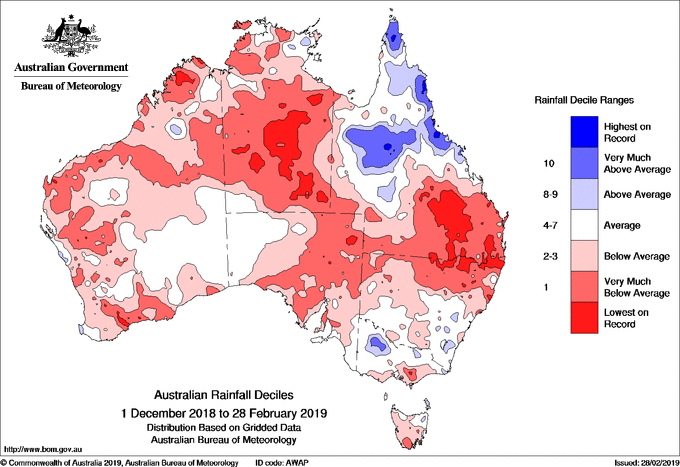
Map: Summer 2018–19 rainfall deciles.
A major rain event affected tropical Queensland during late January to early February, associated with a slow-moving monsoonal low. Some sites had a year’s worth of rain in a two-week period, including Townsville Airport which had 1257 mm in ten days. Many Queenslanders affected by this monsoonal low went from drought conditions to floods in a matter of days. Flooding was severe and continues to affect rivers near the Gulf of Carpentaria, as well as some inland rivers which flow towards Kati Thanda–Lake Eyre.
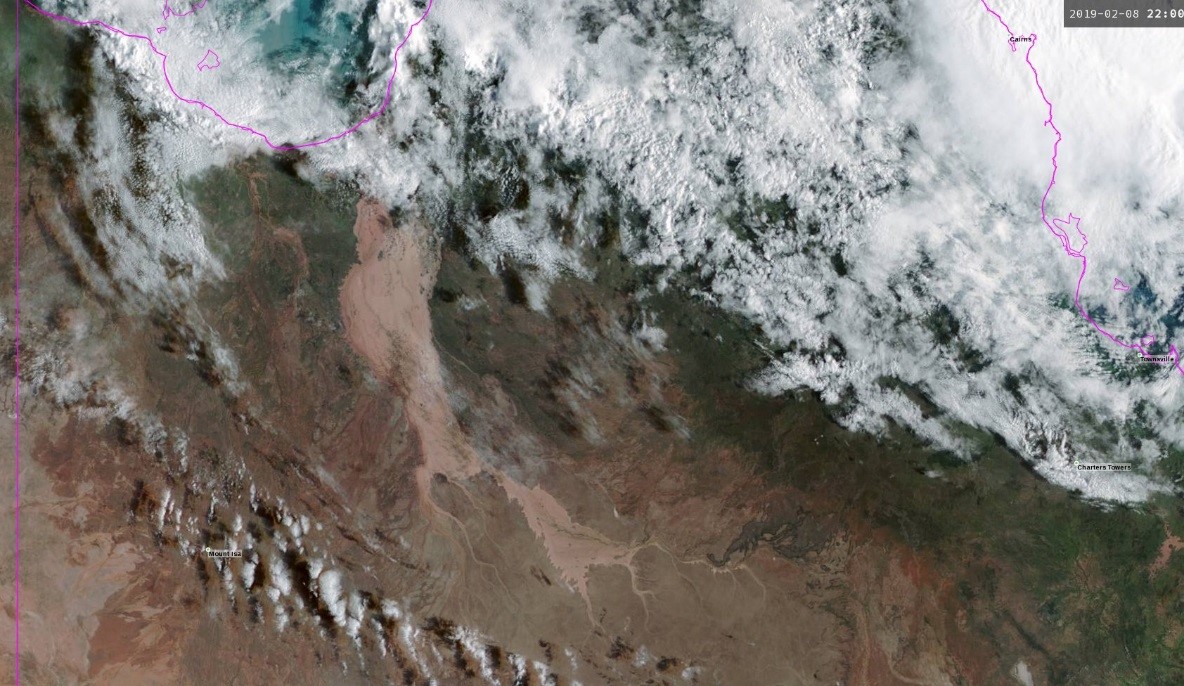
Image: Satellite view of flood waters in western Queensland, showing the Gulf of Carpentaria to the top left (the pink outline shows the coast) and the Coral Sea to the top right.
The outlook for autumn
Spring 2018 saw a positive Indian Ocean Dipole which faded in early summer. At the start of summer sea surface temperature anomalies in the central Pacific exceeded 0.8 °C, which is the typical threshold for El Niño affecting the oceans, but these declined as summer progressed. Combined with a lack of coupling between the atmosphere and ocean, the El Niño–Southern Oscillation remained neutral, though normal rainfall patterns shifted to oceans to the north and east, leaving Australia drier as a result.
As we move into autumn, the El Niño–Southern Oscillation and Indian Ocean Dipole tend to have less influence. The onset of new Indian Ocean Dipole or El Niño/La Niña events typically happens in late autumn or winter/spring.
Over recent years, autumn rainfall has also become less reliable, with declines in cool season rainfall in the southeast and southwest. Temperatures are also rising, in a local expression of the global warming trend.
Our outlook for autumn shows high probabilities that day and night-time temperatures will remain above average for most of the country. We expect to see continued below-average rainfall in much of the east, where drought is currently widespread.
Looking to the winter, the ENSO Wrap-Up suggests the Pacific Ocean is likely to remain warmer than average. The potential for an El Niño remains, with approximately a 50 per cent chance of El Niño developing during the southern hemisphere autumn or winter, twice the normal likelihood.
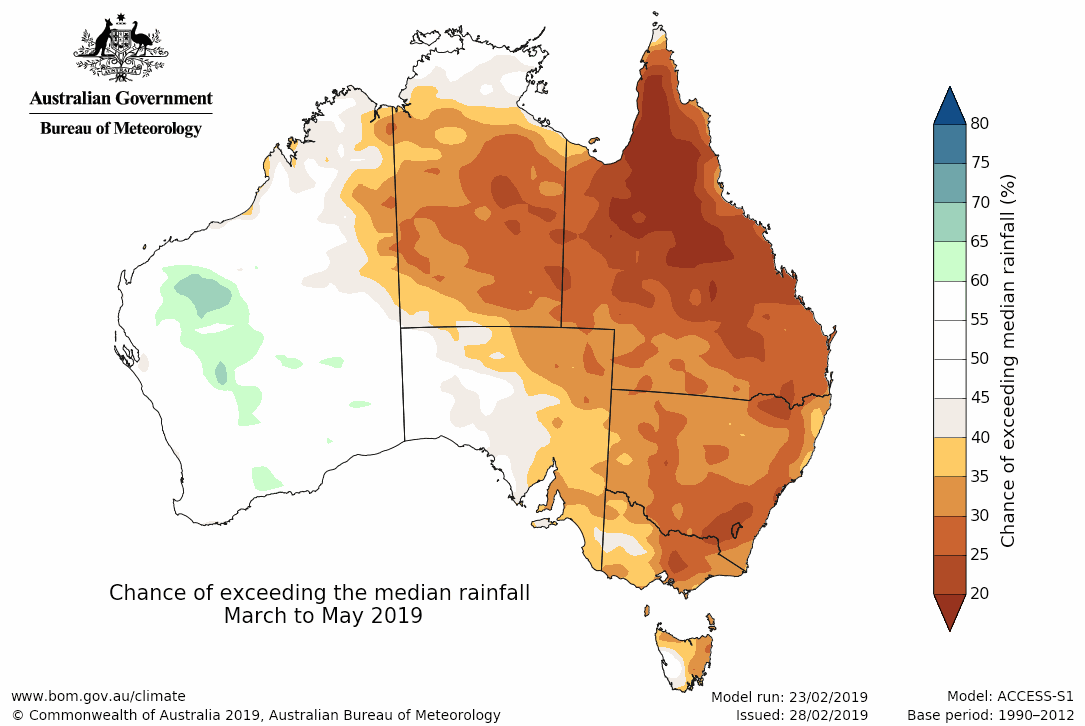
Map: Rainfall outlook for autumn 2019.
More information
Watch our March–May 2019 Climate and Water Outlook video and subscribe to receive Climate Information emails.
For more information on recent conditions, read our Climate Summaries.
The stubborn high-pressure system behind Australia's record heatwaves
Explainer: El Niño and La Niña
Summer 2018-19 was hottest on record, BOM says, with little relief expected for autumn (ABC)
![]()
An earlier version of this article was published on The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.

Subscribe to this blog to receive an email alert when new articles are published.
![]()

Comment. Tell us what you think of this article.
Share. Tell others.