Bureau warns of severe to extreme heatwave conditions this week
12/01/2016
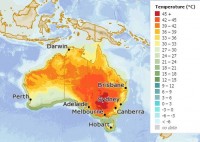
Temperatures are forecast to spike across the country again this week, with severe to extreme heatwave conditions forecast for large parts of Australia.
An extremely hot air mass will see widespread temperatures in the low to mid-40s for inland New South Wales tomorrow (Wednesday).
New South Wales and the ACT can expect to see relief on Thursday as a cool and gusty southerly change moves through the southern and western parts of the state during the day.
While some capital cities will avoid the worst of the heat, Melbourne is forecast to reach a top of 41C tomorrow, before a late cool change will see temperatures dip below 20C.
Adelaide is forecast to reach 39C and Canberra 38C tomorrow, with Western Sydney reaching 41C on Thursday, and Perth 39C on Friday.
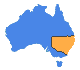
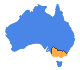
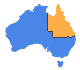
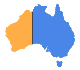
The Bureau now provides a Heatwave Service in addition to the temperature forecast, which provides a measure of the intensity of a heatwave, compared to the long-term climate average.
Mr John Nairn said the Heatwave Service allows the Bureau to inform the community of the severity of a heatwave, and is able to map the level of intensity of each heatwave event.
“The current event shows large areas of Australia will reach severe heatwave conditions, a more advanced indicator than temperature alone in anticipating the impact of heat stress,” said Mr Nairn.
Severe and extreme heatwaves pose significant risks to human health and safety, particularly the elderly, who are more vulnerable to the effects of heat stress.
When temperatures are unusually hot over a period of time, with continuously high night-time and day-time temperatures, heat stress becomes a critical factor in human survival and infrastructure resilience.
Check the Bureau’s website for the latest weather forecasts and warnings, and follow us on Twitter.
Further information on the Bureau’s Heatwave Service for Australia can also be found on our website.